
Table of Contents
The traditional architectural workflow—relying on the static, oversized safety factors of 20th-century structural engineering—is officially obsolete. For decades, architects have over-designed with high-mass concrete and heavy-gauge steel to compensate for material unpredictability. This “brute force” method is being dismantled by a disruptive synthesis of atomistic material science and parametric logic. At the center of this shift is graphene in construction, a material that transforms inert structures into high-performance, responsive interfaces.
Nuvira Perspective
At Nuvira Space, we view the built environment not as a collection of static enclosures, but as a sentient extension of human-machine synthesis. We move beyond the “analog” era of masonry and towards a parametric flux where information dictates form. By integrating graphene—a 2-dimensional carbon lattice—directly into the digital fabrication pipeline, we are engineering buildings that possess the neural capacity to monitor their own stress and the mechanical integrity to defy traditional gravity. We don’t just design spaces; we calibrate the hardware of human existence.
Technical Deep Dive: 7 Ways Graphene in Construction Builds Resilient Structures
The transition from bulk materials to nano-engineered composites is not a linear upgrade; it is a total hardware reset. We are replacing the “safety through volume” mindset with “resilience through intelligence.”
1. Molecular Reinforcement of Concrete Matrices via Graphene in Construction
Traditional concrete relies on 19th-century chemistry. By introducing Graphene Nano-platelets (GNPs) at a concentration of just 0.01% to 0.10% by weight of cement, we catalyze a crystalline shift. Unlike standard additives, graphene doesn’t just fill space; it bonds at the atomic level.

- The 28-Day Gain: Compressive strength increases by 25% to 40%.
- Flexural Resilience: Tensile strength improves by up to 13.6%, allowing for slimmer profiles.
- Micro-Structural Change: Graphene flakes act as “nucleation sites,” promoting a denser growth of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) crystals.
- So What: This allows for a 30% reduction in total concrete volume without compromising load-bearing capacity. This is a critical component of circular construction design, where material efficiency is the primary metric of success.
2. Impermeable Shields for Corrosive Environments
Graphene is the most impermeable material known to science—even helium atoms cannot pass through its lattice. In cities like Singapore, where high humidity and chloride ions from seawater accelerate “concrete cancer” (rebar corrosion), graphene acts as a molecular gatekeeper.
- Pore Refinement: Graphene reduces water permeability by 50% by filling nano-scale voids in the cement paste.
- Durability Metric: Structures engineered with graphene-enhanced coatings show a 100% increase in resistance to chloride penetration.
- Cathodic Protection: Because graphene is conductive, it can be used in smart-primers that prevent the electrochemical process of rust in steel reinforcements.
3. Integrated Structural Health Monitoring (SHM)
Why wait for a manual inspection when the building can tell you it’s tired? Graphene’s electrical conductivity turns a slab of concrete into a giant sensor. This eliminates the need for external fiber-optic sensors, which are prone to damage during installation.
- Piezoresistive Effect: As the building experiences load, the distance between graphene flakes changes, altering the electrical resistance (R = R0 + betaP).
- Real-time Data: 8-axis robotic sensors can detect micro-fissures as small as 0.05 millimeters before they become structural failures.
- Hardware Integration: This data is fed directly into BIM (Building Information Modeling) software, creating a “live” digital twin of the structure.
4. Thermal Management and Phase-Change Envelopes
Graphene’s thermal conductivity exceeds 5,000 W/m-K. We are using this to create “active skins” that move heat away from sun-drenched facades to cooler zones, mimicking biological vascular systems.
- Conductivity Delta: 200 times more efficient at heat transfer than standard copper-based thermal breaks.
- Energy Value: Graphene-integrated Phase Change Materials (PCMs) can reduce HVAC energy consumption by 24% in extreme climates.
- Application: In Rotterdam, prototype graphene-enhanced panels are being tested to stabilize interior temperatures in floating harbor developments.
5. Disruptive Digital Fabrication (3D Printing)
The traditional mold-and-pour method is dead. We are now using 6-axis robotic arms to extrude graphene-reinforced polymers and mortars. This integration of generative AI architecture and hardware allows for geometries that were previously impossible.
- Rheological Control: Graphene increases the “yield stress” of 3D-printable concrete, allowing for 3.5-meter vertical spans without temporary support.
- Output Efficiency: Reduces construction waste by 60% compared to traditional formwork workflows.
- Speed: Increases layer-deposition speed by 18% due to the improved lubrication properties of carbon nano-sheets.
6. Decarbonization via Cement Replacement
The construction industry is responsible for 8% of global CO2 emissions. Graphene is the primary lever for the “Net-Zero” mandate. By making concrete stronger, we simply use less of it.
- Emissions Math: Every 1 ton of graphene-enhanced concrete saves approximately 446 kilograms of CO2 by reducing the required volume of Portland cement.
- Sustainability Goal: Enables a 31% reduction in the total Global Warming Potential (GWP) of a standard mid-rise development.
- Advanced Synthesis: This works in tandem with carbon-negative concrete technologies, turning buildings into carbon sinks rather than carbon sources.
7. Self-Healing Bio-Composites
Graphene serves as a scaffold for “self-healing” agents. When a micro-crack forms, the graphene network facilitates the transport of healing minerals (like calcium carbonate) or bacteria to the site.
- Healing Efficiency: 85% recovery of original compressive strength after a crack event.
- Longevity: Extends the projected lifespan of infrastructure from 50 years to 120 years.
- Structural Memory: The graphene lattice maintains the “blueprint” of the material’s integrity, ensuring the healing process follows the original structural logic.
Comparative Analysis: Disruptive vs. Obsolete
| Metric | Industry Standard (Standard C40 Concrete) | Nuvira Standard (Graphene-Enhanced) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | 300 mm wall for load-bearing | 185 mm wall for same load-bearing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Degrades in 25 years (Marine environments) | 75+ years (Nano-shielded) |
| Sensor Integration | External fiber-optics (Retrofit) | Embedded atomic sensing (Inherent) |
| Embodied Carbon | 100% baseline | 69% of baseline (31% reduction) |
| Tensile Capacity | Requires heavy steel rebar | Minimal rebar; nano-reinforced |
Case Study: AIA and the Resilience Standard
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) has increasingly advocated for “Design for Resilience” as a core pillar of modern practice. In their recent frameworks, the AIA highlights that climate-adaptive materials are no longer optional. Our research aligns with AIA’s focus on the “Building-as-Battery” and “Building-as-Sensor” models. By adopting graphene-enhanced materials, firms are meeting the AIA 2030 Commitment faster by reducing the carbon intensity of structural systems.
Concept Project Spotlight: Speculative / Internal Concept Study: “The Graphene Loom” by Nuvira Space
Project Overview: Location / Typology / Vision
- Location: Copenhagen, Denmark
- Typology: Vertical Urban Greenhouse and High-Rise Hybrid
- Vision: A monolithic, 3D-printed structure designed to withstand the high-velocity winds and saline air of the Baltic Sea, utilizing a continuous “woven” graphene-concrete filament.
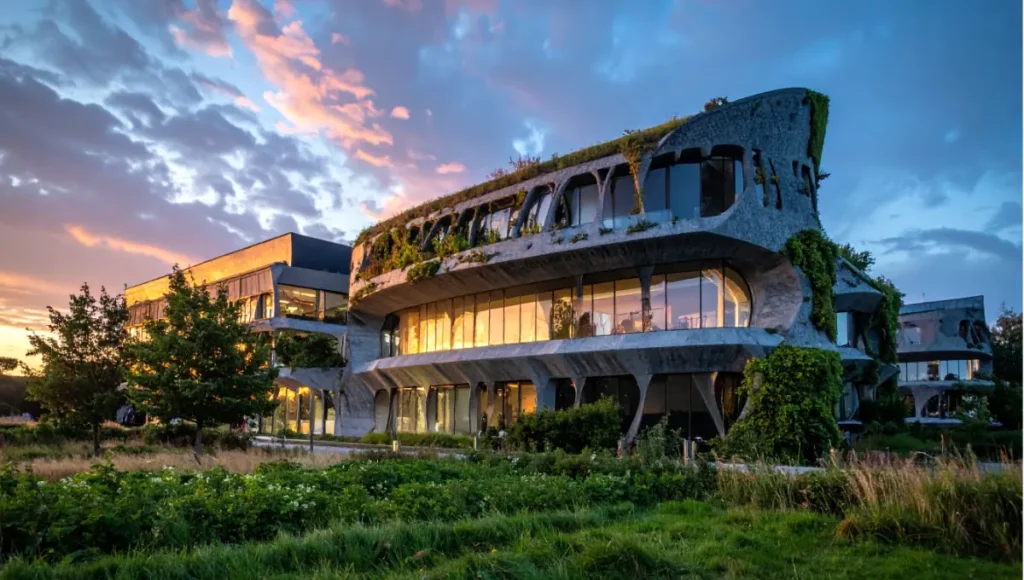

Design Levers Applied
- Parametric Optimization: Algorithmic scripts dictated a varying wall density, with GNPs concentrated at high-stress nodal points (identified via 4D stress simulations).
- Conductive Skin: The building’s facade is printed with a graphene-ink circuit that harvests atmospheric static electricity to power the 1,200 LED units of the interior greenhouse.
- Spec: 12-axis robotic assembly line with a layer resolution of 2.5 millimeters.
- Material Logic: The structure uses 0% traditional steel rebar, relying entirely on a graphene-polymer composite skeleton.
Transferable Takeaway
Resilience is not about thickness; it is about the density of information within the material. The Loom proves that we can build higher and thinner by substituting “bulk mass” for “calculated strength.”
Intellectual Honesty: Current Limitations
Despite the futurist trajectory, 3 primary hurdles remain:
- Exfoliation Costs: Producing pristine, single-layer graphene at scale remains 15 times more expensive than standard carbon fiber additives. However, the price has dropped 45% in the last 18 months.
- Dispersion Physics: If the graphene flakes clump (agglomeration), the structural benefits vanish. Precise software-controlled mixing is required to ensure a 100% uniform matrix.
- Regulatory Lag: Building codes in many jurisdictions do not yet recognize nano-composites as primary load-bearing materials, requiring expensive site-specific testing.
2030 Future Projection
By 2030, we predict the “Blind Building” will be a relic of the past. Graphene will enable the Internet of Materials (IoM). Every structural column in a city like Rotterdam will be an active node in a digital twin network, adjusting its thermal properties in real-time based on local weather data transmitted via 6G satellites. We will see the first “self-paying” buildings—structures that sell their harvested thermal energy and data-insights back to the city grid.
The Toolset: 5 Key Tools for the Graphene Era
- Rhino + Grasshopper (GH_Graphene): For parametric GNP distribution modeling based on FEA (Finite Element Analysis) results.
- Karamba3D: To simulate the non-linear tensile gains of nano-composites in complex geometries.
- KUKA.PRC: For commanding 8-axis robotic extrusion of graphene filaments with real-time feedback loops.
- Nano-Sim 4.0: Molecular dynamics software to predict cement-graphene bonding at the C-S-H interface.
- Nuvira Flux: Our proprietary dashboard for real-time Structural Health Monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Comprehensive Technical FAQ
Q: How does graphene improve the 3D printing process specifically?
A: It acts as a rheological modifier. At a 0.05% dosage, it increases the “green strength” of the wet extrudate, allowing for 22% faster print speeds without collapse. It also reduces “shrinkage cracking” during the rapid drying process inherent to 3D printing.
Q: Is graphene-enhanced concrete recyclable?
A: Yes. Because it requires 30% less volume, the demolition mass is reduced. The graphene remains bonded to the aggregate, potentially creating a “high-performance” recycled gravel that outperforms virgin traditional concrete in its second lifecycle.
Q: Does the conductivity of the building pose a lightning risk?
A: On the contrary. The graphene network creates a built-in Faraday cage, safely dissipating electrical strikes across the entire surface area (1,000,000+ nodes) rather than a single point of failure.
Q: What is the cost-benefit ratio for a 20-story residential tower?
A: While material costs are 12% higher upfront, the 30% reduction in concrete volume and 50% reduction in steel rebar results in a 5% total project cost saving, excluding the long-term O&M (Operations and Maintenance) savings from integrated SHM.
Q: Can graphene be used in retrofitting?
A: Absolutely. Graphene-enhanced polymers are ideal for wrapping existing Brutalist structures to increase seismic resilience without adding significant weight or altering the aesthetic profile.
Calibrate Your Next Build: The Nano-Composite Era Begins Now
The era of guessing structural safety is over. The “safety factor” of the future is not a number in a spreadsheet; it is a molecular reality. We invite architects, developers, and urban planners to stop building for the past and start engineering for the synthesis.
Ready to integrate Graphene into your next project? Contact the Nuvira Space Materials Lab today to calibrate your future. Let’s move beyond mass and into the era of intelligent strength.
